Nanoparticle synthesis
Hot injection, and heat-up
Hot injection:
- one reagent added quickly to boost supersaturation
Heat-up:
- All reactants added together, then heated. Supersaturation reached during this heating.
- Can only hope for this to happen fast enough to have homogeneous and small particles.
LaMer Theory
- Can explain nucleation and growth of NP’s in the abovementioned synthesis routes.
Secondary mechanisms after nucleation
- Coalescence: Particles are fused together to one blob where the original particles are not distinguishable.
- Agglomeration: Particles fused together are still distinguishable.
- Oriented attachment: Particles are fused together is special orientations.
Cobalt NP synthesis
- Made by burst nucleation (hot injection)
- Solvent, surfactant(oleic acid), cobalt precursor, (usually a reduction agent but not for cobalt since its already in ox state 0)
- Cobolt carbonyl decomposes at 50C, so when hot injected it immediately decomposes, and nucleates. Then the surfactants in the hotsoup protect the particles from more growth and coalesence.
Micelles, Inverse Micelles, Vesicles
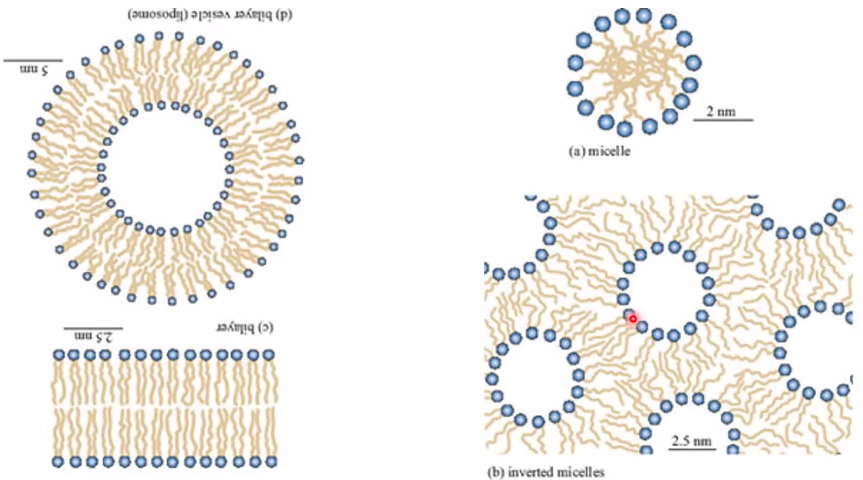 These micelle cavities can be called nanoreactors.
These micelle cavities can be called nanoreactors.
- Size can be tuned by amount of the two liquids (polar/not polar) and the surfactant How are vesicles made? Almost philosophical question, because it might be the start of life as we know it.