Electrode reactions
Faradays law
- The amount (moles) of any substance produces or consumed in an electrode reaction is proportional to the quantity of charge passed.
- Non-faradaic currents:
- Capacitive currents
- Electronic conduction
- Competing reactions
Coulometry
- Analysis of concentration c\(_i\) of a reactant species \(i\) in a finite volume V at fixed well-selected voltage
- The total charge converted is Q = -nFVc\(_i\)/\(\nu_i\)
- n av \(\nu_i\) are te number of electrons and molecules, respectively, involved in the reaction
- Charge Q is current \(I\) integrated over time t:
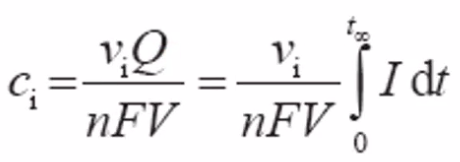
- Flowing coloumetry
- Limiting current at given flow and fixed voltage.
Butler-Volmer equation
Example:
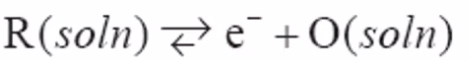
- Butler-Volmer:

- \(k^{\circ}\) is a formal rate constant
- Positive term says