Electrochemical power
Chemical (Gibbs) energy to electrical energy
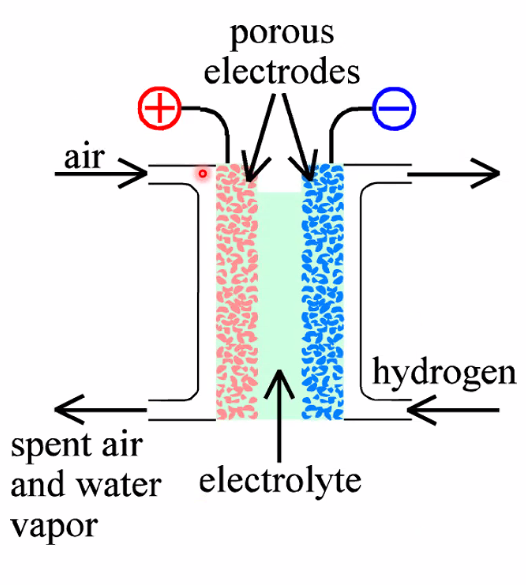
Fuel cells
- Fuels: H\(_2\), Reformed CH\(_3\)OH, Reformed CH\(_4\)
- Electrolytes: Alkaline, Acid(Phosphoric acid and PEM), Molten carbonate, Solid oxide(Y-doped Zr), Proton ceramic(oxides with dissolved water)
Batteries:
- Primary (one time use)
- Dry cell
- NH\(_4\)Cl + ZnCl\(_2\) paste
- C in powder composite cathode
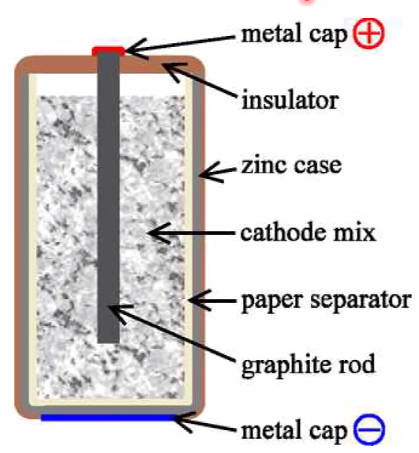
- Alkaline battery (most used today)
- Negative: \(\mathrm{Zn}(s)+2 \mathrm{OH}^{-}(a q) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{ZnO}(s)+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)\)
- Positive: \(\mathrm{MnO}_{2}(s)+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{MnOOH}(s)+\mathrm{OH}^{-}(a q)\)
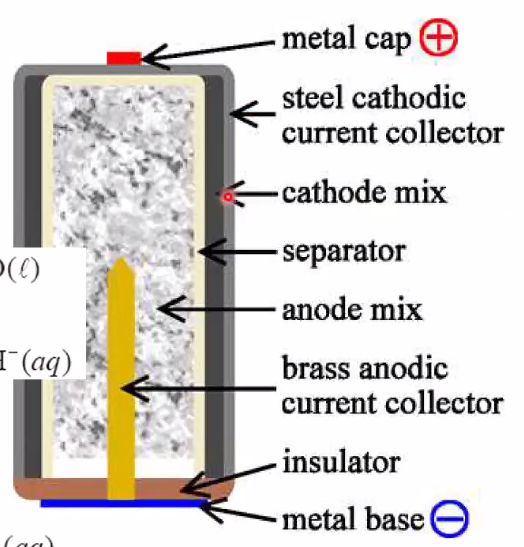
- Other alkaline positrodes:
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{HgO}(s)+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Hg}(\ell)+2 \mathrm{OH}^{-}(a q) \\ \mathrm{Ag}_{2} \mathrm{O}(s)+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ag}(s)+2 \mathrm{OH}^{-}(a q) \\ \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}(g)+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{OH}^{-}(a q)\end{array}\right.\)
- Dry cell
- Secondary (rechargeable)
- Lead acid:
- Corrosion of the positive (Pb(s)) electrode
- Oxygen evolution from the positive electrode (H2O -> H3O)
- Hydrogen evolution at the negative electrode (H3O-> H2O)
- Oxygen reduction at the negative electrode (O + H3O -> H2O)
- Lead acid:
- Primary (one time use)
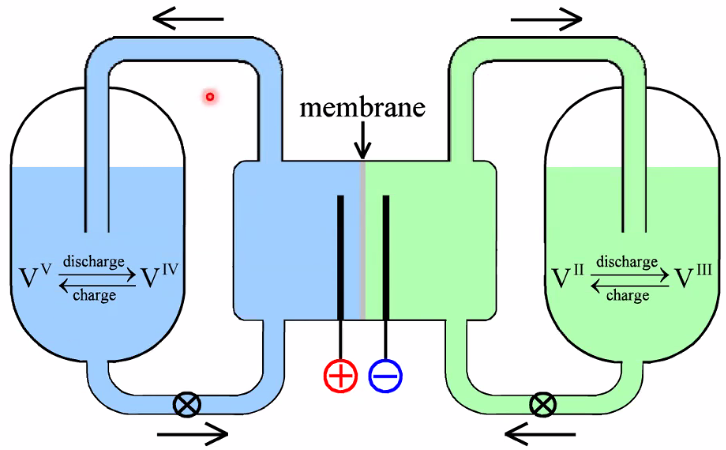
Redox flow battery
Positive: \(\mathrm{VO}_{2}^{+}(a q)+2 \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}(a q)+\mathrm{e}^{-} \underset{\text { recharge }}{\stackrel{\text { discharge }}{\leftrightarrows}} \mathrm{VO}^{2+}(a q)+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\ell)\)
Negative: \(\mathrm{V}^{2+}(a q) \underset{\text { recharge }}{\stackrel{\text { discharge }}{\rightleftarrows}} \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{V}^{3+}(a q)\)